

The global business landscape of 2025 stands at a critical juncture where technological innovation must align with environmental responsibility. While artificial intelligence and automation dominate headlines, a quieter revolution is unfolding in simulation technology—one that promises not just operational excellence but unprecedented environmental impact. Yet despite simulation technology’s remarkable potential to slash carbon footprints across industries, this sustainability dimension remains dramatically underutilized, representing perhaps the greatest missed opportunity in our fight against climate change.
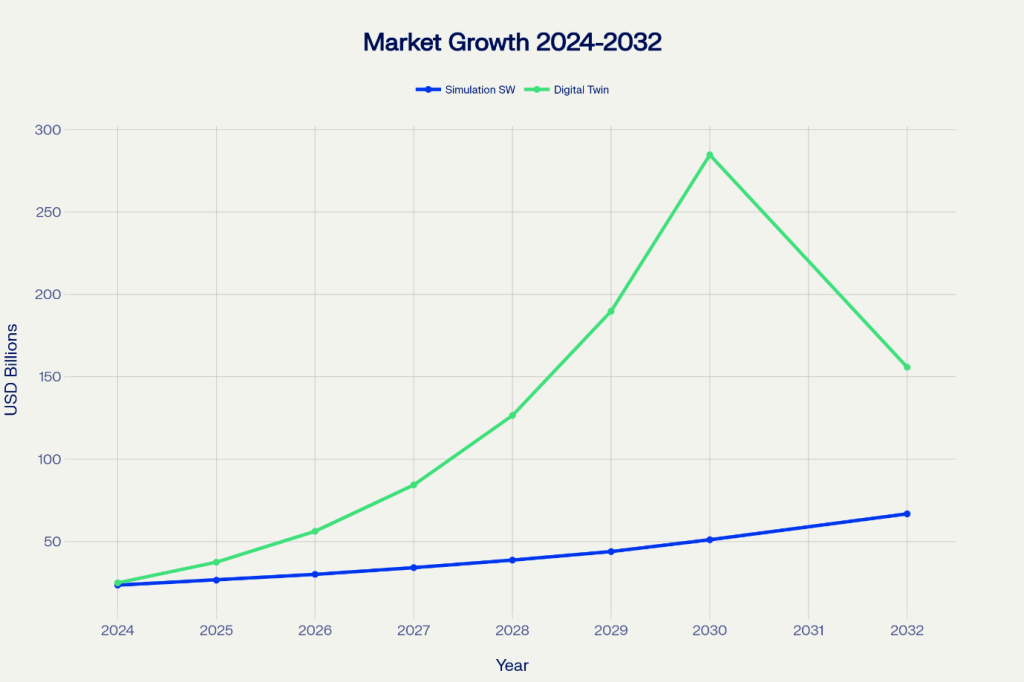
The simulation technology market is experiencing unprecedented expansion, with the global simulation software market projected to reach $51.11 billion by 2030, growing at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.0%. Even more striking is the digital twin market, which is expected to explode from $37.50 billion in 2025 to an astounding $284.76 billion by 2030, representing a staggering 47.9% CAGR.
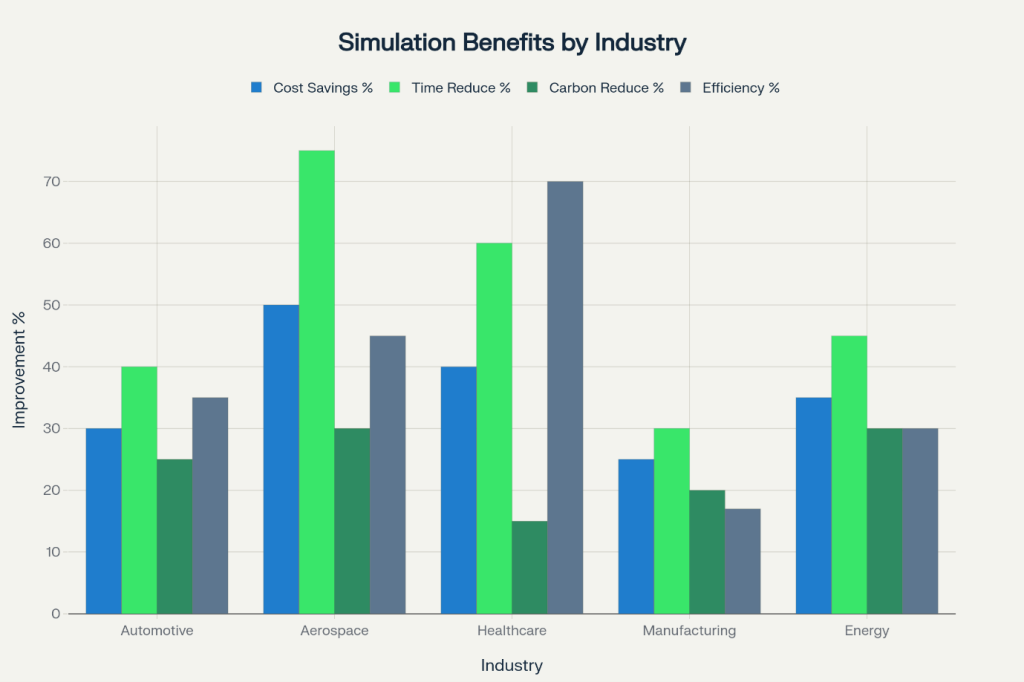
The energy sector achieves 35% cost savings and 45% time reduction through simulation implementation. Digital twins in energy management can reduce consumption by 25-30%, with some facilities reporting energy use cuts of up to 25%, material waste reduction of 17%, and CO2 emissions decrease of 25%.
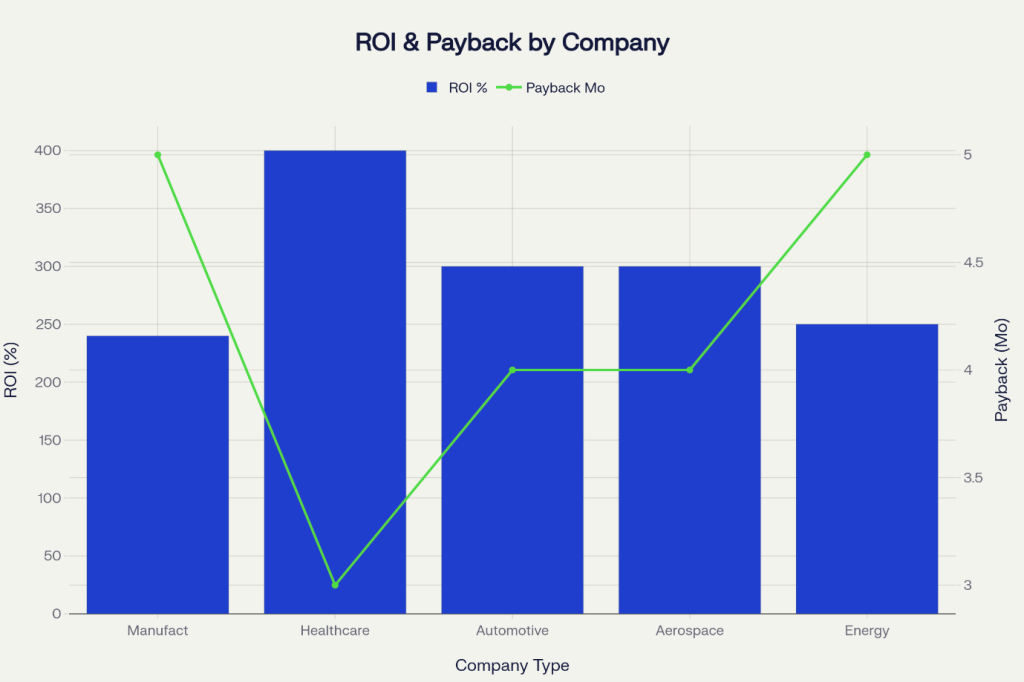
The financial benefits of simulation technology are not just impressive—they’re transformative. Analysis of multiple case studies reveals an average ROI of 298% with payback periods averaging just 4.2 months. These figures represent some of the strongest returns on investment available in today’s technology landscape.
Healthcare training shows the most dramatic returns, with some implementations achieving 400% ROI in just 3 months. Manufacturing plants typically see 240% ROI within 5 months, while aerospace testing delivers 300% ROI in 4 months. These consistent, high-return results across diverse industries underscore simulation technology’s universal applicability and value.
AT&T’s $250 million workforce transformation investment through simulation-based training resulted in a 25% increase in revenue over five years and 45% decrease in employee turnover. Similarly, IBM’s annual $1 billion training investment, heavily leveraging simulation, produced a 318% increase in revenue per employee over a decade.
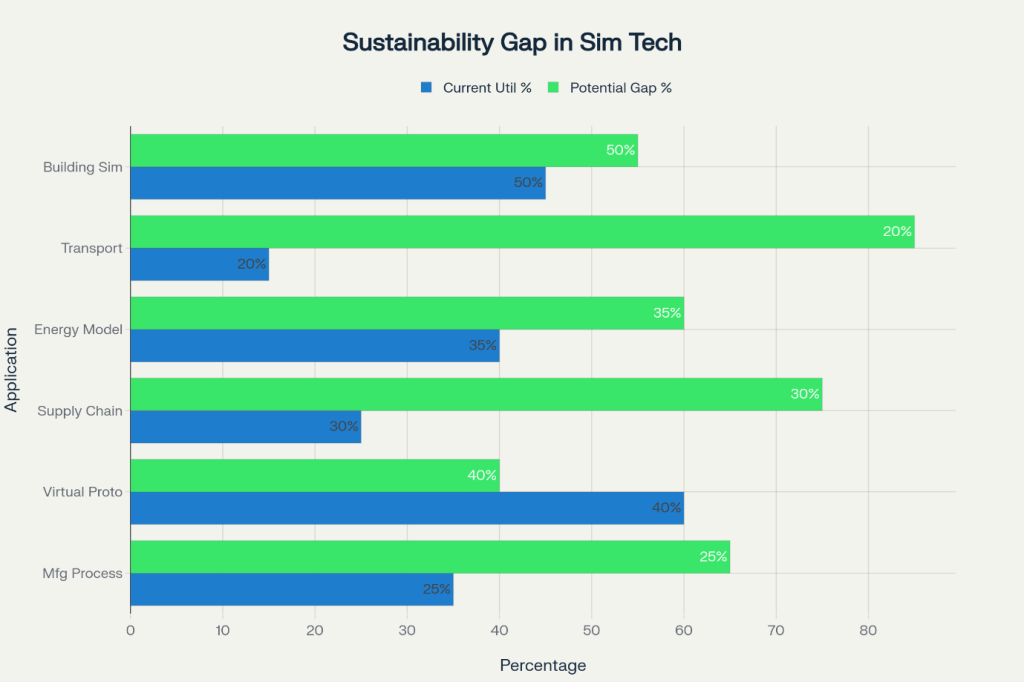
The building sector, responsible for 26% of global carbon emissions (approximately 9.6 Gt CO2), could achieve 20% energy bill reduction through simulation-based optimization. When scaled globally, these reductions represent thousands of gigawatts of energy savings and millions of tons of avoided CO2 emissions.
Several factors contribute to this sustainability blind spot:
The year 2025 marks a pivotal moment for simulation technology integration. Cloud-based simulation adoption has exploded, with AnyLogic 9 enabling web-based modeling and real-time collaboration. AI-powered simulation is becoming standard, with ChatGPT integration providing real-time insights and data analysis capabilities.
The convergence of 5G, IoT, and edge computing is enhancing digital twin capabilities, enabling real-time data streaming with updates occurring every 30 seconds. This technological fusion creates unprecedented opportunities for continuous environmental optimization.
Investors increasingly consider ESG criteria, with over 80% of mainstream investors now factoring sustainability information into investment decisions. Companies implementing comprehensive sustainability strategies report up to 10% reduction in capital costs, making simulation’s environmental benefits financially material.
The simulation software market will experience sustained growth, reaching $51.11 billion by 2030. More dramatically, the digital twin market is projected to explode to $149.81-284.76 billion by 2030, representing one of the fastest-growing technology segments.
Smart Cities and Urban Planning: Digital twins will optimize urban energy consumption by 15% and reduce infrastructure costs by 20-25% by 2030. Cities worldwide are investing billions in smart infrastructure, with simulation technology providing the backbone for optimization.
Climate Risk Management: Advanced simulation models will become essential for predicting and mitigating climate-related disasters, with AI-powered platforms like Sipremo already demonstrating 20-30% emissions tracking improvement.
Circular Economy Implementation: Simulation will enable sophisticated modeling of circular business models, optimizing resource flows and minimizing waste across entire value chains.
By 2030, sustainability considerations will become primary drivers of simulation adoption rather than secondary benefits. Several trends support this prediction:
A leading electronics manufacturer faced decisions about automated guided vehicle (AGV) fleet sizing for a new television assembly line. Traditional approaches would have required extensive physical testing and multiple equipment purchases for optimization.
Simulation Solution: Dijitalis created a comprehensive digital twin modeling the entire production line, AGV paths, and material flows.
Environmental Impact: The optimized AGV system reduced energy consumption equivalent to removing 200 cars from roads annually.
Westinghouse needed to optimize complex production scheduling across multiple nuclear fuel manufacturing facilities while maintaining stringent safety and quality standards.
Simulation Solution: Integration of multiple facilities in a single digital twin with detailed routing logic and real-time constraint management.
Results:
Traditional Training Challenges:
Simulation Solution: Implementation of advanced simulators like Anti-Aircraft Air Defence Simulator (3ADS).
Results:
Environmental Impact: Annual carbon footprint reduction equivalent to thousands of tons of CO2 while maintaining training effectiveness.
With global manufacturing responsible for 33% of total carbon emissions and 40% of energy consumption, simulation technology represents a critical decarbonization tool. If just 50% of manufacturers implemented comprehensive simulation for process optimization, the potential impact includes:
The transportation sector’s adoption of simulation for route optimization and fleet management could deliver:
With buildings accounting for 26% of global carbon emissions, simulation-based design optimization could achieve:
The evidence is overwhelming: simulation technology offers unprecedented opportunities for operational efficiency AND environmental impact reduction. Yet this dual benefit remains largely unrecognized, representing perhaps the greatest missed opportunity in corporate sustainability efforts.